
IntensiChem Hydrogenation Development
- Commonly used to reduce or saturate organic compounds.
- Typically, the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, such as an alkene.
- Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable.
- Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.
- Non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures.
- The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst.
- Traditional methods in batch use catalysts supported on carbon.
These are difficult or cannot be used in flow. This is because the carbon can crush under pressure resulting in fines that build up and clog the flow.
The solution is to use Flow chemistry with a packed bed made up of liquid chromatography media such as alumina or silica as a support for the catalyst.
- As a result, the process of hydrogenation is highly suited to the Flow Chemistry approach.
IntensiChem and Hydrogenation
IntensiChem's flow hydrogenation technology:
- Exploit high temperatures, up to 250’C, normally. Can operate at 500’C.
- Operate at high pressures, up to 100Bar, normally. Possible up 1000Bar.
- Have precisely controlled, short reaction times.
- IntensiChem's approach delivers higher yields, and greater process efficiency.
- IntensiChem can take current batch processing and develop an efficient continuous flow process using its unique skillset.
- The cost of continuous flow dedicated plant is significantly less than for traditional batch manufacturing techniques.
- Reactor volumes are very much smaller than those used in batch. This results in a very much safer operating, negating the need for a "explosion-proof bunker" approach.
- IntensiChem understands fully the barriers to scale-up, and has already demonstrated scale-up from the lab to Plant scale.
High Performance Fixed Bed
- Fixed bed with catalyst particles typically less than 100um.
- Use of high pressure pumps.
- Control of hydrogen injection rate.
- Tight residence time distribution.
- Suitable for complex pharmaceutical products.
Summary of Driving Principles
- High pressure – gas concentration proportional to pressure.
- Small particles – High gas surface area.
- High temperature – Gas concentration increases with temperature.
- Effective control of mass transfer.
- Enabling commercial scalability.
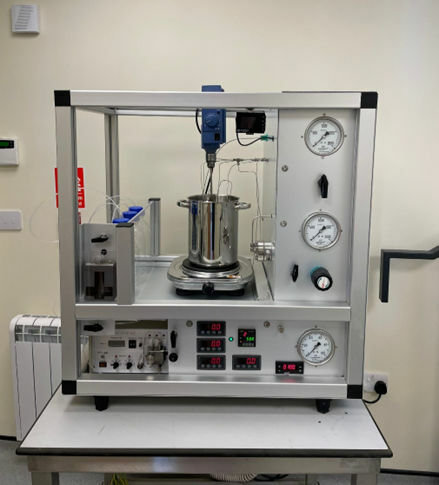
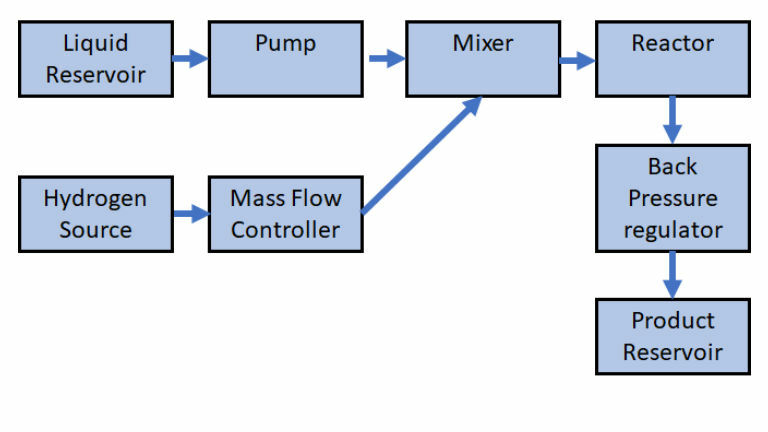

Hydrogenation Development System
- IntensiChem will carry out process development and optimisation studies to fully understand the appropriate catalysts, temperatures, pressures and reaction times to allow complete and efficient production of the desired product.
- IntensiChem's novel technology enables efficient hydrogenation in seconds, significantly reducing the size and cost of commercial reactors.
- Our technology can achieve a better and safer commercial conversion using reactors of only a couple of litres of volume, in contrast to standard batch reactors with volumes of thousands of litres.